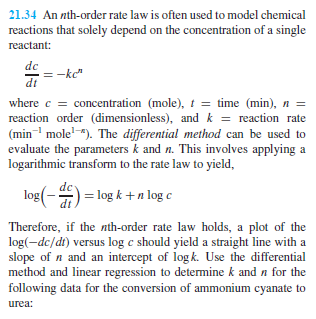
21.34 An nth-order rate law is often used to model chemical reactions that solely depend on the concentration of a single reactant: de: –kc” dit where c = concentration (mole), t = time (min), n = reaction order (dimensionless), and kreaction rate min mole”). The differential method can be used to evaluate the parameters k and n. This involves applying a logarithmic transform to the rate law to yield, log( ) -log k+n log c
OR
OR
